Abstract
Background: TAFA is a CD19-directed monoclonal antibody approved in combination with LEN for the treatment of adult patients with R/R DLBCL who are not eligible for transplant. As the number of available CD19-directed therapies, including CAR-T, for patients with DLBCL increase, the optimal sequencing of such therapies needs to be established. Here we present a series of 8 cases of patients with R/R DLBCL who received treatment with TAFA+LEN followed by CAR-T therapy. The objectives of the case series are to describe demographic and clinical characteristics, treatment patterns and outcomes, and CD19 testing and expression in these patients.
Methods: All patients were treated in routine clinical practice at the authors' institutions. Included patients had a R/R DLBCL diagnosis, received at least 1 administration of TAFA+LEN, were ≥18 years of age upon initial TAFA+LEN administration, and subsequently went on to receive CAR-T therapy. Patients' clinical characteristics, treatment sequence and details, and outcomes of therapy were described qualitatively.
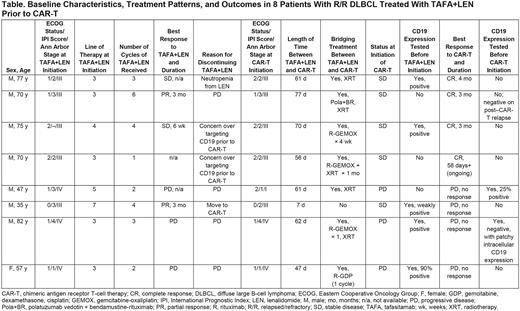
Results: Eight patients were included; baseline characteristics, treatment patterns, and outcomes are summarized in the Table. All patients were White and ranged in age from 35 to 82 years; all but one were male. Three patients had germinal center B-cell (GCB) disease, 4 had non-GCB disease, and 1 was unknown. Two patients had bulky disease (>7.5 cm) at diagnosis. TAFA+LEN was the third-line of therapy in 5 patients, the fourth-line of therapy in 1 patient, and later-line in 2 patients. Treatment and clinical outcome immediately prior to receiving TAFA+LEN varied; 3 patients had achieved a best response of complete response (CR) after their last line of therapy, 1 achieved a partial response (PR), 2 had stable disease (SD), and 2 had progressive disease (PD). The median time until disease progression after completion of prior treatment was 16 months (range 2-24 months; n=4 patients with available data).
Among the 8 patients, the best overall responses on TAFA+LEN were PR in 2 patients, SD in 2 patients, and PD in 3 patients (1 patient was not evaluable). Reasons for discontinuing TAFA+LEN were PD (4 patients), choice to move to CAR-T therapy (3 patients), and neutropenia (1 patient). Median time between TAFA+LEN and subsequent CAR-T therapy was 61 days (range 7-77). Seven of the 8 patients received treatment with chemotherapy, radiotherapy, or other therapies, alone or in combination, between TAFA+LEN and CAR-T. Five patients had SD at CAR-T initiation, while 3 patients had PD. CRs to CAR-T were seen in 4 patients; 3 patients subsequently progressed after CRs of 3-4 months' duration, and 1 patient had ongoing CR at 58 days. No response to CAR-T (ie, PD) was observed in 4 patients.
CD19 testing was performed on fresh biopsy from 5 patients before initiation of TAFA+LEN; all were positive (weakly positive in 1 patient). CD19 testing was performed on fresh biopsy from 2 patients before CAR-T initiation; 1 patient was 25% positive on tumor cells and 1 patient was negative for CD19 expression with patchy intracellular expression-neither patient responded to CAR-T. Fresh biopsy was obtained from 1 patient after progression following CAR-T therapy and was negative for CD19 expression.
Conclusions: Among these 8 patients with R/R DLBCL, 2 each achieved PR or SD with TAFA+LEN, 3 had PD, and 1 was not evaluable for response. Following treatment with TAFA+LEN, 4 patients had a subsequent CR to CAR-T therapy, in line with expectations from pivotal clinical trials of approved CAR-T agents (Westin JR, et al. Am J Hematol. 2021;96:1295-1312). In this small case series, there does not appear to be an impact of prior use of TAFA+LEN on the effectiveness of subsequent CAR-T therapy in patients with R/R DLBCL. Only 2 patients had CD19 expression evaluated prior to CAR-T therapy-one was negative and one was 25% positive; neither patient responded to CAR-T therapy. Further research is needed to determine the optimal sequencing of CD19-directed therapies TAFA+LEN and CAR-T in patients with R/R DLBCL.
Disclosures
Veeraputhiran:KITE pharma: Speakers Bureau. Mehta:AstraZeneca: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Speakers Bureau; TG Therapeutics: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding, Speakers Bureau; Takeda: Research Funding; Kite/Gilead: Consultancy, Research Funding; Merck: Research Funding; Roche-Genentech: Research Funding; Pharmacyclics: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Speakers Bureau; Incyte: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding, Speakers Bureau; Kyowa Kirin: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Speakers Bureau; Juno pharmaceuticals/BMS: Consultancy, Research Funding; Innate pharmaceuticals: Research Funding; Seattle Genetics: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding, Speakers Bureau; BeiGen: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Speakers Bureau; Norvartis: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Speakers Bureau; fortyseven Inc./Gilead: Consultancy, Research Funding, Speakers Bureau; I-MAB: Research Funding; Celgene/BMS: Consultancy, Research Funding, Speakers Bureau; Affimed: Research Funding; BMS: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Speakers Bureau; Gilead: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Speakers Bureau; Morphosys/Incyte: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Speakers Bureau; Seattle Genetics: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding, Speakers Bureau. Alencar:Celgene: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Incyte: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; BeiGene: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Loxo Oncology: Research Funding; TG Therapeutics: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Karyopharm: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Janssen: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; OncLive: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Amgen: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Kite Pharma: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Epizyme: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; SeaGen: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees. Modi:Seagen Inc.: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Genentech: Research Funding; MorphoSys: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; ADC Therapeutics: Research Funding; Karyopharm Therapeutics: Research Funding; AstraZeneca: Honoraria; Beigene: Speakers Bureau. Voorhees:Incyte: Research Funding; AstraZeneca: Research Funding. Narkhede:Genetech: Research Funding; Roche: Research Funding; Gilead: Research Funding; Gilead/Forty-seven: Research Funding; EUSA pharmaceuticals;: Research Funding; ADC Therapeutics: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Seagen Inc.: Research Funding; Genmab: Research Funding; TG Therapeutics: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal